The
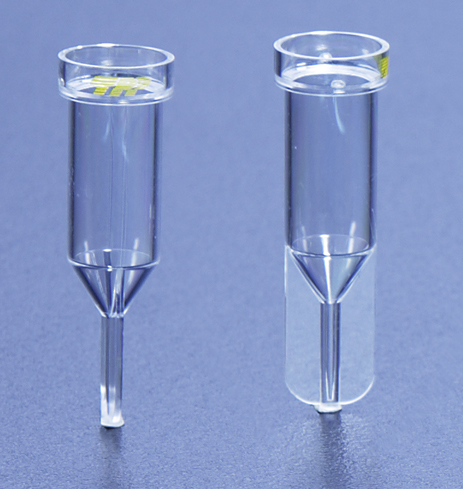
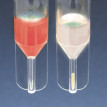
PCV tube enables a quick and reproducible measuring technique of the cell volume. This method is ideal for the monitoring of the tissue growth (cell mass).
If during a production process many parameters need to be optimized, many samples accumulate at the same time. Here a quick analysis with the PCV tube and the read-out process with „easy read“ is the method of the choice.
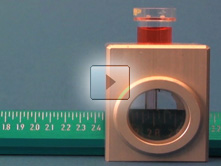
A short centrifugation step (1 minute at 2'500 gx) is sufficient to form a pellet in the calibrated capillary. There the pellet can be read with the “easy read” measuring device
Features of the PCV tube:
- PCV tube with calibrated capillary, some available with volume graduation
- Fits in micro-centrifuges
- Caps available
Determination of cell number density is a routine task in almost every laboratory working with cell cultures. The most commonly used method is counting cells manually with the hemacytometer, which is very time-consuming, tedious and prone to errors (margin of error about 15 %).
The PCV-system provides a fast, easy to use, reproducible and more accurate alternative to manual cell counting. The PCV-tubes enable the determination of the packed cell volume (PCV) in a cell suspension, resulting in absolute data correlating with parameters like protein content, cell count, metabolic activity and others.
The PCV-tubes are particularly convenient to work with, requiring neither special training nor sophisticated expensive machines – in contrast to automated cell counting devices.